A former security engineer, who stole digital assets valued at more than $12 million from two decentralized exchanges, has received a three-year prison sentence. In what has been characterized as the “first-ever” conviction for a smart contract hack, the U.S. Judge also ordered the ex-engineer to forfeit roughly $12.3 million. Ex-Engineer Sentenced to Three Years […]
A former security engineer, who stole digital assets valued at more than $12 million from two decentralized exchanges, has received a three-year prison sentence. In what has been characterized as the “first-ever” conviction for a smart contract hack, the U.S. Judge also ordered the ex-engineer to forfeit roughly $12.3 million. Ex-Engineer Sentenced to Three Years […]
Source link
decentralized
Velar Launches Dharma AMM to Propel Bitcoin Into the Decentralized Finance Spotlight
 On Tuesday, the bitcoin liquidity protocol Velar unveiled Dharma, an automated market maker (AMM) designed to enhance decentralized finance liquidity within the Bitcoin realm. The inaugural version of Velar’s Dharma is set to function on the Bitcoin layer two (L2) Stacks, featuring an initial pairing of two tokens. Velar’s Strategy to Elevate Bitcoin Within the […]
On Tuesday, the bitcoin liquidity protocol Velar unveiled Dharma, an automated market maker (AMM) designed to enhance decentralized finance liquidity within the Bitcoin realm. The inaugural version of Velar’s Dharma is set to function on the Bitcoin layer two (L2) Stacks, featuring an initial pairing of two tokens. Velar’s Strategy to Elevate Bitcoin Within the […]
Source link
ceτi AI Announces Successful Launch of Revolutionary Decentralized AI Infrastructure Token
 ceτi AI, a pioneering decentralized artificial intelligence infrastructure provider, is thrilled to announce the successful launch of its CETI token. Founded by a team of visionaries led by Dennis Jarvis (formerly of Bitcoin.com and Apple), ceτi AI is on a mission to democratize access to AI by building a globally distributed, high-performance, intelligent, and scalable […]
ceτi AI, a pioneering decentralized artificial intelligence infrastructure provider, is thrilled to announce the successful launch of its CETI token. Founded by a team of visionaries led by Dennis Jarvis (formerly of Bitcoin.com and Apple), ceτi AI is on a mission to democratize access to AI by building a globally distributed, high-performance, intelligent, and scalable […]
Source link
ECB Economists: Bitcoin Fails to Become Global Decentralized Digital Currency, BTC’s Fair Value Is Still Zero
 The European Central Bank (ECB) has published a blog post claiming that “bitcoin has failed to fulfill its original promise to become a global decentralized digital currency.” The ECB economists who authored the post added that bitcoin’s fair value is still zero and bitcoin transactions are “still inconvenient, slow, and costly.” Moreover, they asserted that […]
The European Central Bank (ECB) has published a blog post claiming that “bitcoin has failed to fulfill its original promise to become a global decentralized digital currency.” The ECB economists who authored the post added that bitcoin’s fair value is still zero and bitcoin transactions are “still inconvenient, slow, and costly.” Moreover, they asserted that […]
Source link
BNB Chain Reveals Basic Principles, Features and Roadmap for Its Greenfield Decentralized Storage Network
The recent updates for BNB Greenfield contains extensive details on its roadmap, basic principles, and features that support AI adoption.
BNB Chain has published an official tech roadmap for BNB Greenfield, a decentralized storage network for data decentralized applications (dApp) operating in the BNB ecosystem. The roadmap contains several interesting developments that combine Web2 performance and Web3 features to improve user experience.
Basic Principles and Features of the BNB Greenfield Roadmap
BNB Chain created the Greenfield roadmap based on three design principles. The first is for the blockchain to have such high performance that it competes favorably with most Web2 offerings. This way, transactions, and other on-chain activities are processed faster. While ensuring that the blockchain is high-performance, the second design principle – a simplified development experience – guarantees that the Greenfield platform is user-friendly and accessible. This way, navigating BNB Greenfield will be easy for developers regardless of experience level.
The third principle is that while BNB Greenfield is a BNB Chain platform, it functions as a multi-chain network. Developers would be able to create multiple blockchains and design projects with seamless interaction between dApps on different blockchains. In addition to this interaction, users will also enjoy several other cross-chain services.
The Roadmap describes extensive features tied to each of these principles. For instance, the high-performance principle seeks to significantly improve transaction speed. With the current download and upload speeds at 20MB/s and 2MB/s, respectively, the aim is to 5x these numbers. In addition, there is a bundle service for data handling, which allows users to organize multiple data files into single blockchain objects for better processing.
The second principle offers improved storage features, like sorting and organizing data using tags. These tags help users move and update large amounts of data without confusion. For the third principle, the exciting feature is cross-chain programmability. This gives smart contracts more flexibility as they currently do not allow others to use their resources. BNB Greenfield solves this problem by introducing a cross-chain permission module.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Stability, and Network Governance
All of BNB Greenfield’s features lay the groundwork for AI adoption. The decentralization, innovation, and transparency enjoyable on BNB Greenfield are features that facilitate AI adoption and create an enabling environment for AI and Web3 integration.
The overarching aim is to ensure that access and use of BNB Greenfield is easy and affordable for all interested parties, including developers, storage providers, and regular users. Storage providers will enjoy “lightweight architecture”, with low computational requirements, sparse device footprint on the network, and reduced energy consumption. Despite all of that, BNB Greenfield has a simple exit process for all storage providers who would like to withdraw their deposits and exit the platform.
The specific Roadmap for BNB Greenfield will see the platform begin in Q4 this year by simplifying the exit process for storage providers and enabling features that allow smart contracts to function as “resource owners”, for robust permission control. The next course of action is to improve storage provider performance while increasing upload and download speeds by 5x in Q2/Q3 2024. The Web3 AI adoption comes next and may stretch past 2024.
next
Binance News, Blockchain News, Cryptocurrency News, News
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
American Cancer Society leverages Gitcoin for decentralized open-source cancer research funding

In a move that blends innovation with philanthropy, the American Cancer Society (ACS) has embraced web3 technology by partnering with Gitcoin, a leading figure in open-source funding, according to a statement shared with CryptoSlate.
This strategic collaboration signifies a milestone for the ACS as it steps into the decentralized world of web3, leveraging Gitcoin’s expertise to drive its ACS Cares program and the Crisis Response Fund.
The ACS round, distinct and independent from the regular seasonal Gitcoin Grants program, is designed to benefit the ACS Cares program and the Crisis Response Fund directly. This initiative is crucial, as donations will be channeled towards groundbreaking cancer research, advancing health equity initiatives, and bolstering patient support programs.
Additionally, it will aid in providing essential lodging for cancer patients undergoing treatment. This venture represents a crucial intersection of technology and philanthropy, where blockchain’s potential is harnessed for impactful healthcare outcomes.
The initiative represents a continued interest in decentralized open-source funding by a renowned non-profit organization utilizing Gitcoin technology. The first instance was a significant QF collaboration pilot with UNICEF in 2022.
Gitcoin and decentralized funding.
The significance of Gitcoin in the realm of open-source funding cannot be overstated. Since its inception, Gitcoin has played a pivotal role in the web3 ecosystem, mainly through its utilization of Quadratic Funding (QF). This innovative funding mechanism has enabled Gitcoin to disperse over $50 million across more than 100 rounds, empowering organizations like UNICEF and now the ACS in their mission-driven endeavors.
QF is central to Gitcoin’s strategy, a crowdfunding approach that values the number of contributors over the total donation amount. This method fosters widespread community involvement and ensures equitable allocation of funds to projects that resonate most with the public. In the case of the ACS round, this methodology promises to channel resources efficiently towards breakthrough cancer research, health equity initiatives, and patient support programs, all pivotal in the fight against cancer.
Azeem Khan, Head of Impact at Gitcoin, commented,
“By using Gitcoin, the American Cancer Society gains access to a vibrant community of technologists and crypto enthusiasts who are passionate about driving positive change.
This partnership combines Gitcoin’s expertise in blockchain with the American Cancer Society’s commitment to cancer research and prevention, creating a powerful synergistic effect in the fight against cancer.”
Azeem Khan added, “Participating in the ACS round powered by Grants Stack is a unique opportunity for individuals and organizations to contribute to the fight against cancer with blockchain technology.”
Kyle Weiss, Executive Director at the Gitcoin Foundation, and Nicole d’Avis, Protocol Lead at the Public Goods Network (PGN), have both expressed enthusiasm for these collaborative efforts. The PGN, an innovative project in the Gitcoin ecosystem, operates as a low-cost Layer 2 OP Chain, directing most of its net sequencer fees towards public goods. This initiative presents a cost-effective alternative to the Ethereum mainnet for users and developers, simultaneously generating funds for public goods through transactions.
While open-source funding may not have captured mainstream media attention, entities like Gitcoin and PGN have quietly revolutionized how public goods are supported. Their efforts are instrumental in creating sustainable and reliable funding sources for initiatives that serve the greater good.
The American Cancer Society’s venture into web3 with Gitcoin is more than a fundraising initiative; it is a beacon of innovation in the philanthropic world. By adopting blockchain technology and leveraging the power of community-driven funding, the ACS is furthering its mission to combat cancer and setting a precedent for other non-profits to explore the transformative potential of web3.

As expectations grow that a spot Bitcoin exchange-traded fund (ETF) will be approved in the United States, it remains one of the hottest topics heading into 2024. In Episode 38 of Cointelegraph’s Hashing It Out, Elisha Owusu Akyaw talks to Joel Kuck, CEO of Decentralized ETF (D-ETF), about how ETFs work, the potential impact of spot Bitcoin (BTC) ETFs on the cryptocurrency industry and the idea of decentralized ETFs.
Amid the optimism that U.S. regulators are set to greenlight multiple spot BTC ETFs, some projects are also looking to bring other ETFs to the blockchain while riding the wave of hype around the investment products. Kuck explains why the industry is bullish about spot Bitcoin ETFs and why the excitement around them is mounting.
He explains that direct exposure to Bitcoin for institutional investors and funds through spot ETFs will boost adoption, which wasn’t previously feasible because some investors were unwilling to touch Bitcoin directly and be responsible for the self-custody of their assets.
According to Kuck, ETFs are an important wealth management and investment instrument that must be available for people in developing markets. He explains that this is the background for the creation of decentralized ETFs. This new classification of ETFs intends to take traditional ETFs to the blockchain, providing exposure for users who would otherwise not have access due to their jurisdiction or other barriers.
As 2023 comes to an end, Hashing It Out guests are asked to share their thoughts about the future of crypto and give their projections for 2024. Kuck said he is bullish that we will see a spot Bitcoin ETF soon and multiple similar products in the next five years. Moreover, he expects an increase in the tokenization of real-world assets, and the opening up of fractional ownership of assets like real estate powered by the blockchain.
Listen to the full episode of Hashing It Out on Apple Podcasts, Spotify or TuneIn. You can also explore Cointelegraph’s full roster of informative podcasts on the Cointelegraph Podcasts page.
Magazine: Slumdog billionaire — Incredible rags-to-riches tale of Polygon’s Sandeep Nailwal
This article is for general information purposes and is not intended to be and should not be taken as legal or investment advice. The views, thoughts, and opinions expressed here are the author’s alone and do not necessarily reflect or represent the views and opinions of Cointelegraph.

In the rapidly evolving realm of DeFi, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) stand as a cornerstone, enabling seamless transactions in a trustless environment.
At the heart of these exchanges lies the mechanism of order matching, a crucial process that pairs buyers with sellers, facilitating the exchange of assets. Traditionally (on order book-based exchanges), order matching has been centralized, with a single entity overseeing the process to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
However, the advent of blockchain technology has paved the way for decentralized order-matching systems, promising to align DEXs with the ethos of decentralization further.
Centralized and decentralized order batchers are central to this discussion, each representing a different approach to order matching.
Understanding centralized order matching
Centralized order matching operates under the aegis of a central authority that oversees the matching of buy and sell orders. This setup collects orders within a defined time frame and batches them together. Once the batch is complete, a centralized matching engine sifts through the orders, pairing buyers with sellers based on predefined criteria such as price and time of order placement.
Advantages
- Efficiency: The centralized nature of batchers ensures a streamlined process, often resulting in faster order matching and execution. This is particularly beneficial in high-frequency trading environments where speed is of the essence.
- Accuracy: With a single entity overseeing the process, the likelihood of errors is significantly reduced, ensuring accurate order matching.
- Ease of management: Centralized systems often come with a well-defined administrative structure, making it easier to manage, monitor and rectify issues should they arise.
Disadvantages
- Centralization risk: The central authority becomes a single point of failure. In the event of a system breakdown or malicious activity, the integrity of the entire order-matching process is compromised.
- Privacy concerns: Centralized systems require participants to entrust their data to the central authority, which could deter privacy-conscious users.
- Lack of control: Traders have to relinquish control over the order-matching process, which could be at odds with the decentralized ethos that DEXs aim to uphold.
Centralized order matching through batchers presents a tried-and-tested mechanism, providing a level of efficiency and accuracy crucial for a seamless trading experience. However, the inherent centralization poses risks and challenges that may not align with the decentralization narrative prevailing in the DeFi space.
As DEXs evolve, the quest for alternative, decentralized order matching systems gathers pace, with smart order routers (SORs) emerging as a potential contender in this decentralized narrative.
Delving into decentralized order matching
Decentralized order matching, symbolized by smart order routers, embodies the essence of decentralization, where the process is distributed among participants within the network rather than being controlled by a singular entity.
In this setup, SORs autonomously match bids and ask order from the onchain order book and make profits on the spread
Advantages
- Decentralization: With no central authority, SORs epitomize the core ethos of decentralization, minimizing the risks associated with significant points of failure.
- Transparency: The decentralized nature of smart order routers ensures a higher degree of transparency as all transactions are recorded on the blockchain and visible to all participants.
- Self-Custody: Traders retain control over their orders, aligning with the tenets of user sovereignty central to DEXs.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: The decentralized setup can introduce a level of complexity that might be daunting for less tech-savvy individuals.
- Potential latency: Decentralized systems might experience a slight delay in order execution compared to their centralized counterparts, especially in networks with high congestion.
- Resource intensity: The continual search for optimal order routing across diverse liquidity pools can be resource-intensive.
Smart order routers highlight the potential of decentralization in order matching, aligning with the broader goals of transparency and user control within DEXs.
However, complexity and potential latency challenges underline the need for robust decentralized infrastructures to support seamless order execution.
Comparing options
The juxtaposition of centralized and decentralized order-matching systems through the lens of batchers and smart order routers unveils a spectrum of considerations.
On one end, the efficiency, accuracy and administrative ease offered by centralized systems like batchers is alluring, especially in a high-frequency trading landscape. However, the centralization risks and privacy concerns would be considered drawbacks to some.
Conversely, smart order routers pave the way for a decentralized order-matching paradigm, resonating with the core tenets of transparency and user control inherent in DEXs. Yet, the hurdles of complexity and potential latency cannot be overlooked.
Efficiency vs. decentralization: Batchers provide a streamlined and efficient process at the cost of centralization. Smart order routers, while decentralized, may introduce additional latency and complexity.
Security and transparency: The decentralized nature of SORs offers enhanced security and transparency, minimizing central points of failure, unlike centralized systems that may pose data privacy concerns.
User experience: Centralized systems may offer a more straightforward user experience, while decentralized systems offer user control but with added complexity.
Impact of blockchain technology: Blockchain technology is the linchpin that enables decentralized order matching, with smart contracts playing a pivotal role in automating and securing the process.
The discourse between centralized and decentralized order-matching systems symbolizes the broader dialogue within the DeFi space, encapsulating the trade-offs between efficiency, user control and decentralization.
As DEXs mature, exploring hybrid models that encapsulate the merits of both worlds might emerge as a pathway toward optimizing order matching in decentralized landscapes.
Conclusion
The discourse surrounding centralized and decentralized order matching, epitomized by batchers and smart order routers, underscores a pivotal juncture in the evolution of DEXs.
The trade-offs between efficiency, transparency, user control and complexity are emblematic of the broader challenges and opportunities within the DeFi space. As DEXs strive to balance the core ethos of decentralization with the pragmatic need for efficiency and user-friendly interfaces, exploring these order-matching systems becomes instrumental.
As DEXs evolve, hybrid models that encapsulate the merits of centralized and decentralized order-matching systems may emerge, potentially heralding a new era of optimized, user-centric and resilient decentralized trading platforms.
The information provided here is not investment, tax or financial advice. You should consult with a licensed professional for advice concerning your specific situation.
CSO at Genius Yield, a next-generation DEX & CEO at gomaestro.org a Web3 infrastructure provider
This article was published through Cointelegraph Innovation Circle, a vetted organization of senior executives and experts in the blockchain technology industry who are building the future through the power of connections, collaboration and thought leadership. Opinions expressed do not necessarily reflect those of Cointelegraph.
Learn more about Cointelegraph Innovation Circle and see if you qualify to join
French regulator sees DeFi as ‘disintermediated,’ not ‘decentralized’

On Oct. 12, the Autorité de Contrôle Prudentiel et de Résolution (ACPR), part of the French Central Bank, published a summary of its public consultation on a regulatory framework for decentralized finance (DeFi).
The public consultation lasted two months, from April to May 2023, in response to the initial paper discussing possible regulations for DeFi in the country. External contributions nudged the ACPR to surprising revelations, especially regarding the structural persistence of centralization patterns:
“The ACPR therefore believes that the term ‘disintermediated’ finance is more appropriate than that of ‘decentralized’ finance.”
The operational risk of this “paradoxical high degree of concentration” in DeFi concerns the physical infrastructure hosting blockchain nodes, in which cloud service providers play a central role.
Related: CBDC lays foundation for new global monetary system: French central bank
According to the summary, the “vast majority” of respondents advocate that DeFi should continue to be deployed on public blockchains rather than on private or permissioned ones. However, they admit that these blockchains need to be audited on a regular basis. Proposals to regulate intermediaries and certify smart contracts were also met with broad consensus.
In conclusion, the ACPR finds it “advisable” to draw up rules for the certification of smart contracts, define governance that would protect DeFi customers, and lay down measures supporting DeFi’s blockchain infrastructures.
On Oct. 11, the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) also weighed in on the discussion on DeFi. In a 22-page report, the ESMA admitted the promised benefits of DeFi, such as greater financial inclusion, the development of innovative financial products and the enhancement of financial transactions’ speed, security and costs, while also highlighting its “significant risks.”
Collect this article as an NFT to preserve this moment in history and show your support for independent journalism in the crypto space.
Magazine: Beyond crypto: Zero-knowledge proofs show potential from voting to finance
Decentralized exchange volumes slump for six months to lowest levels since January 2021
Trading volumes on decentralized exchanges (DEX) have slumped for six consecutive months to their lowest levels since January 2021.
Volume on DEXs decreased to $44.28 billion in September, the sixth consecutive monthly decrease and the lowest recorded volume since January 2021, according to DefiLlama data.
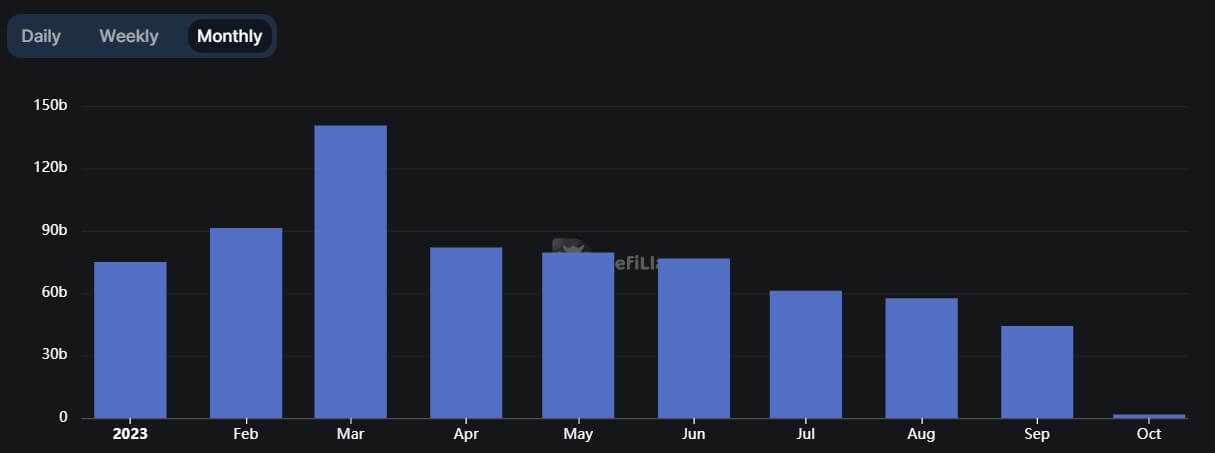
During the first quarter of this year, DEXs experienced a surge in monthly trading activity. This growth was precipitated by increased regulatory scrutiny directed at their centralized counterparts, including major platforms like Kraken, Bittrex, Coinbase, and Binance.
As a result of these regulatory measures, crypto traders migrated their activities towards DEX protocols. In March, trading volume on these decentralized platforms reached an impressive $140 billion. However, this spike was short-lived, with volumes plummeting to around $82 billion in April.
Subsequently, trading activities on these DEXs have been on a consistent decline.This decline can be attributed to a combination of factors, including overall market conditions and the ongoing regulatory pressures facing the industry.
For context, the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) filed charges against three DeFi protocols, including Opyn, Deridex, and ZeroEx. The regulator alleges they illegally offered unregistered derivatives trading products on their platforms.
Additionally, these platforms have regularly been victims of hacks and exploits, making it difficult for users to trust them with their assets.
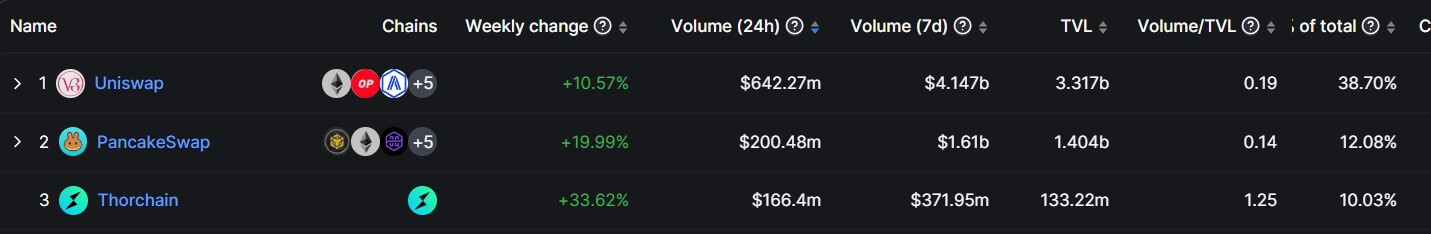
Uniswap remains the dominant decentralized exchange platform despite the falling volume across the board. The protocol contributes more than 38% of the daily volume, and its cumulative volume is three times higher than its closest rival, PancakeSwap.
Meanwhile, trading activity on centralized crypto exchanges is also seeing a downturn. According to available data, trading volume on these platforms fell by 26% to $311.93 billion in September, marking the lowest level since November 2020.
The post Decentralized exchange volumes slump for six months to lowest levels since January 2021 appeared first on CryptoSlate.