 Economist and gold bug Peter Schiff has warned that something big is happening that very few investors are prepared for. “More importantly, governments and central banks are not prepared for it either,” he stressed. Schiff explained that Fed rate cuts will make the inflation problem worse. Peter Schiff’s Warnings Economist and gold bug Peter Schiff […]
Economist and gold bug Peter Schiff has warned that something big is happening that very few investors are prepared for. “More importantly, governments and central banks are not prepared for it either,” he stressed. Schiff explained that Fed rate cuts will make the inflation problem worse. Peter Schiff’s Warnings Economist and gold bug Peter Schiff […]
Source link
prepared
Coinbase says custodial arm has ‘extensively prepared’ for spot Bitcoin ETF

Coinbase Custody has made adjustments in preparation for its role in pending spot Bitcoin ETFs, Bloomberg reported on Dec. 29.
A Coinbase representative said:
“We have extensively prepared for ETF approval … Our systems have been designed and tested to handle added trading volume, increased liquidity and general increases in demand on our systems.”
Part of those changes involve executive reshuffling, according to Bloomberg. Aaron Schnarch, CEO of Coinbase Custody, reportedly stepped down. He has been replaced by Rick Schonberg, an employee of Coinbase since 2021 who has previously held roles in traditional finance including at Goldman Sachs.
Financial institutions are generally required to store cryptocurrency with a qualified custodian, such as Coinbase Custody, rather than with a retail exchange. Bloomberg noted that multiple ETF applicants including including BlackRock, Franklin Templeton, and Grayscale Investments plan to work with Coinbase Custody to manage Bitcoin holdings for their ETFs.
VanEck incidentally named Coinbase Custody as a possible additional custodian in its latest update, though it primarily will rely on Gemini for custody.
Apart from Coinbase Custody’s role as custodian, many ETF applications added Coinbase itself in surveillance-sharing agreements this summer. That role has seemingly helped to satisfy regulators’ concerns over market manipulation.
Several last-minute amendments have arrived
Coinbase Custody’s latest statements arrive alongside several last-minute amendments from spot Bitcoin ETF applicants. BlackRock and Valkyrie submitted updates identifying authorized providers, while VanEck submitted an amendment affirming its reliance on cash creation and redemption models.
Invesco, Fidelity, WisdomTree, and Bitwise additionally filed amendments on Dec. 29. Ark Invest, Grayscale, and Pando Asset AG have filed updates since Dec. 21.
Dec. 29 also marks the last day for spot Bitcoin applicants to modify their filing. The SEC must reach a decision on whether to approve Ark Invest’s spot Bitcoin ETF by Jan. 10, 2024. It may approve other applications at that time.
Hong Kong financial regulators are prepared for spot crypto ETF applications

Hong Kong’s Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) and the Monetary Authority (HKMA) announced their readiness to accept applications for spot crypto exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in a circular released on Dec. 22.
The regulators stated:
“The SFC and the HKMA have reviewed their existing policy for intermediaries which wish to engage in virtual asset-related activities (VA-related activities). The policy is updated in light of the latest market developments, where the SFC has authorised VA futures ETFs and is prepared to accept applications for the authorisation of other funds with exposure to virtual assets, including virtual asset spot exchange-traded funds (VA spot ETFs).”
This action aligns with the recent trend in Hong Kong towards embracing favorable regulations for the crypto sphere. The Asian country has proactively positioned itself as a crypto-friendly hub, introducing various initiatives to foster growth within the industry.
Last month, CryptoSlate reported that Julia Leung, the CEO of SFC, hinted that the regulator would consider allowing retail investors to trade spot crypto ETFs if these investments comply with local regulations.
Spot-based ETFs have garnered significant attention in recent months within the crypto community. Major financial players like BlackRock and Grayscale have filed applications for a spot-based Bitcoin ETF with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
However, despite widespread optimism regarding these ETFs, the SEC has yet to approve any application. Instead, the regulatory body has postponed its decision until the following year.
SFC outlines regulatory measures for Hong Kong ETFs
A separate SFC circular detailed the requirement for the regulator to consider approving an ETF application in Hong Kong.
According to the regulator, transactions by the ETFs must occur through SFC-licensed crypto platforms or authorized financial institutions that comply with HKMA’s regulatory requirements.
The regulator also noted that it would permit both in-kind and in-cash subscription and redemption models for these spot ETFs.
On custodial requirements, the SFC specified that the fund’s trustee or custodian should only delegate crypto custody functions to an SFC-licensed VATP or entities meeting the crypto custody standards outlined by the HKMA.
For the valuation of these spot virtual assets, fund management companies must implement an indexing method reliant on the trade volume of virtual assets across prominent trading platforms.
Is extreme weather still extreme when it seems like it’s happening every day? Whether it is oppressive heat, bitter cold, catastrophic floods or ferocious wildfires, we are all feeling the effects of an angry climate.
Beyond disrupting our lives, the economic impact of these events is deep and pervasive. It is no wonder that companies are now considering climate risks as they decide where to locate or expand their facilities.
“If you have to close for a certain number of days out of the year because of exposure to flood, or if part of your business uses outdoor recreation or outdoor workers, and you have to close because of heat, people are responding to this. And they’re picking places to locate based on lower exposure to these types of climate risks,” said Jeremy Porter, head of climate implications for the non-profit, non-partisan First Street Foundation, which quantifies climate risks for companies, individuals and governments.
Because sustainability is now a part of competitiveness, CNBC considers it in our annual America’s Top States for Business rankings. Under our 2023 methodology, it is part of our Infrastructure category.
To determine which states are the most sustainable — and which are the least — we use state-level data provided to CNBC by First Street on the percentage of properties at risk of major damage from extreme heat, wind, flooding and wildfires over the next 30 years.
We also consider the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)’s Climate Extremes Index, which looks at temperatures, precipitation, drought and hurricanes. And, because companies are looking for sustainable energy sources, we consider U.S. Department of Energy data on renewable power.
Some states are in good shape to handle whatever the climate throws at them, but these are the states most at risk.
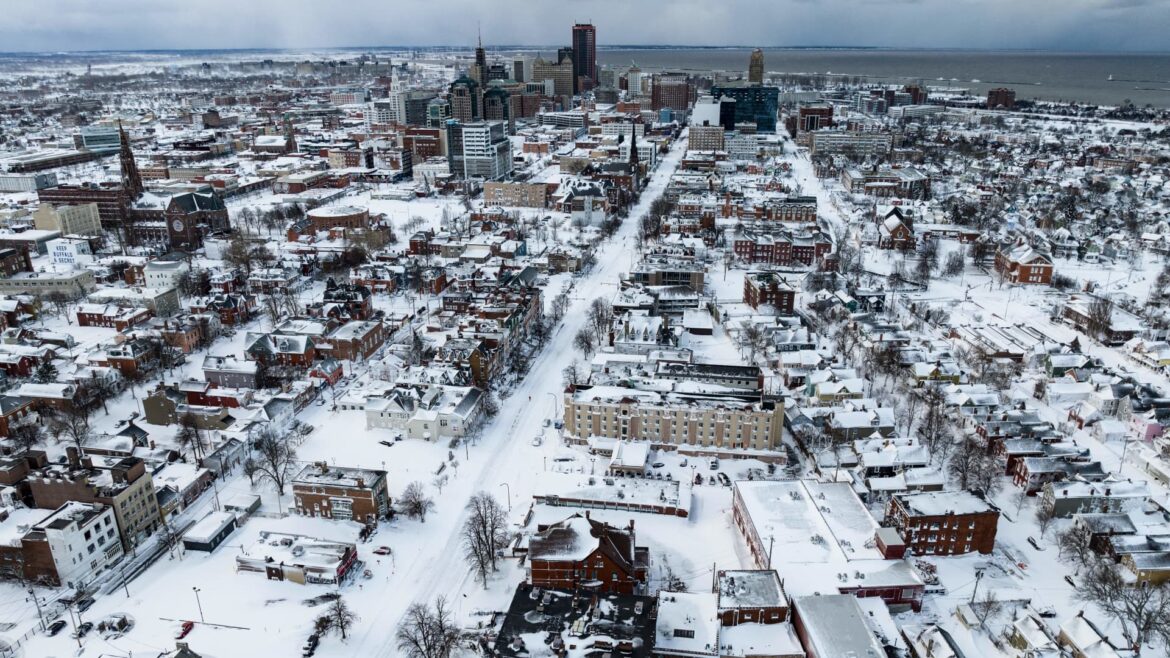
10. (tie) New York
Snow blankets the city in this aerial drone photograph in Buffalo, New York, on December 25, 2022.
Joed Viera | Afp | Getty Images
Christmastime last year was anything but peaceful in the Empire State. Beginning December 23 and continuing for nearly a week, what the National Weather Service described as a “once-in-a-generation” event pummeled the state — and most of the Northeast — with massive snowfalls, blizzard conditions, and flooding. In New York alone, 43 people died. The state prides itself on abundant renewable power. It is a major reason Micron Technology said it chose Syracuse for a massive, $100 billion chip manufacturing plant. But extreme weather here is a concern.
2023 Infrastructure score: 222 out of 390 points (Top States grade: B-)
Climate Extremes Index (National Average: 19.68%): 24.6%
Properties at risk: 21.5%%
Renewable energy: 33.8%
10. (tie) Alabama
TUSCALOOSA, AL – APRIL 28: In the aftermath of a severe tornado, Kelly Giddens (R) helps University of Alabama law student Daniel Hinton remove belongings from his destroyed home in the Cedar Crest neighborhood on April 28, 2011 in Tuscaloosa, Alabama.
Jessica Mcgowan | Getty Images News | Getty Images
Tornado Alley, the swath of the nation’s midsection where most twisters occur, has been gradually shifting eastward, scientists agree. That is bad news for Alabama, which is increasingly in the crosshairs of severe storms. Where in the past, northeastern Texas and southern Oklahoma were most at risk, storms are becoming more prevalent in the Southeast, like a major outbreak in Alabama in March that left one person dead. So far in 2023, the National Weather Service reports 91 tornadoes in Alabama — second only to Illinois — in a state that already faces risks from Gulf Coast hurricanes.
2023 Infrastructure score: 228 out of 390 points (Top States grade: B)
Climate Extremes Index: 21.16%
Properties at risk: 45.2%
Renewable energy: 10.6%
9. Wisconsin
A young girl wades along a flooded street April 19, 2001 in Prairie du Chien, WI.
Tim Boyle | Hulton Archive | Getty Images
While the Badger State has largely escaped major weather disasters in recent years, Wisconsin faces growing risks of flooding, like the incident in April, triggered by heavy rain and snowmelt, that led Gov. Tony Evers to declare a state of emergency. Wisconsin is a big ethanol producer, but the state gets only a small percentage of its energy from renewable sources.
2023 Infrastructure score: 165 out of 390 points (Top States grade: D)
Climate Extremes Index: 8.7%
Properties at risk: 2.8%
Renewable energy: 12%
8. South Carolina
Rain from Hurricane Ian floods a street on September 30, 2022 in Charleston, South Carolina.
Scott Olson | Getty Images News | Getty Images
Hurricane Ian, which ravaged Florida and the Carolinas last year, is the third costliest storm on record. By the time it made its final landfall near Georgetown, South Carolina, on September 30, it did $113 billion in damage and killed 161 people, mostly in Florida. As a coastal state, South Carolina is vulnerable to Atlantic hurricanes, which are increasing in intensity as ocean waters warm.
2023 Infrastructure score: 240 out of 390 points (Top States grade: B+)
Climate Extremes Index: 21.16%
Properties at risk: 46.4%
Renewable energy: 8.8%
7. California
Houseboats sit in a narrow section of water in a depleted Lake Oroville in Oroville, California on September 5, 2021.
Josh Edelson | AFP | Getty Images
The Golden State prides itself on environmental consciousness. It gets much of its energy from renewables, and Gov. Gavin Newsom raised eyebrows — and warmed the hearts of environmentalists —when he ordered that all cars and trucks sold in the state be zero emission vehicles by 2035. Nonetheless, California is beset with climate risks. Its historic drought finally ended this year, but only after record rains drenched the state, causing massive floods and at least 22 deaths. Because the state lacks the infrastructure to capture much of the water for future droughts, trillions of gallons simply flowed out to sea. The rains also led to huge growth of vegetation, which is drying out and becoming a serious fire hazard.
2023 Infrastructure score: 205 out of 390 points (Top States grade: C+)
Climate Extremes Index: 41.04%
Properties at risk: 26.7%
Renewable energy: 74.1%
6. Pennsylvania
A rig drills for natural gas at a hydraulic fracturing site owned by EQT Corp. located atop the Marcellus shale rock formation in Washington Township, Pennsylvania, U.S., on Thursday, Oct. 31, 2013.
Bloomberg | Bloomberg | Getty Images
The Keystone State is rich in fossil fuel resources — second only to Texas in proven natural gas reserves thanks to the massive Marcellus Shale. And the state has a long heritage of coal mining. All of that might help explain why the state is such a laggard in renewable energy. In 2019, then-Governor Tom Wolf established the GreenGov initiative to wean Pennsylvania from fossil fuels. Gov. Josh Shapiro has continued the programs, but progress is slow.
2023 Infrastructure score: 223 out of 390 points (Top States grade: B)
Climate Extremes Index: 24.6%
Properties at risk: 18.9%
Renewable energy: 4%
3. (tie) New Jersey
Flood damaged cars are seen at the Oakwood Plaza Apartments in the aftermath of flooding that was caused by the remnants of Tropical Storm Ida which brought drenching rain, flash floods and tornadoes to parts of the northeast in Elizabeth, New Jersey, September 2, 2021.
Brendan McDermid | Reuters
Nearly two years after the remnants of Hurricane Ida brought flooding and tornadoes to the Garden State, New Jersey is still dealing with the aftermath. Twenty-three people died in New Jersey alone, most due to flooding in the central part of the state. New Jersey’s coastal location makes it particularly vulnerable to intensifying Atlantic storms.
2023 Infrastructure score: 212 out of 390 points (Top States grade: C+)
Climate Extremes Index: 24.6%
Properties at risk: 49.3%
Renewable energy: 11.3%
3. (tie) Delaware
(L to R) Richard Bunting and Alex Hamilton inspect a house that a large tree fell on after a tornado spawned by Hurricane Irene touched down, on August 28, 2011 in Lewes, Delaware.
Mark Wilson | Getty Images
The First State shares most of the sustainability issues of its Mid-Atlantic neighbors. As a coastal state, Delaware is frequently in the path of Atlantic storms and Nor’easters — and as the nation’s second smallest state after Rhode Island, there are not many places to flee to. Despite President Joe Biden’s push for renewable energy, his home state does not set a very good example.
2023 Infrastructure score: 216 out of 390 points (Top States grade: B-)
Climate Extremes Index: 24.6%
Properties at risk: 53%
Renewable energy: 8.2%
3. (tie) Connecticut
In this photo taken using a drone, the blades of a 100-kilowatt, wind-powered turbine spin in the breeze in New Haven, Connecticut on Wednesday, November 11, 2020.
Ted Shaffrey | AP
The Constitution State is aggressively pushing to develop its renewable energy industry. Connecticut is home to the nation’s first “green bank,” which uses public dollars to leverage private investment in renewable energy. The state’s so-called Renewable Portfolio Standard requires electricity providers to offset a set percentage of the energy they generate by purchasing renewable fuel credits. The mandate goes up to 28% next year. The idea is to give them a financial incentive to produce renewable energy themselves, but that is not happening in large numbers yet.
2023 Infrastructure score: 190 out of 390 points (Top States grade: C-)
Climate Extremes Index: 24.6%
Properties at risk: 41.1%
Renewable energy: 8%
2. Florida
A man walks past homes that collapsed onto the beach due to the storm surge and resulting erosion caused by Hurricane Nicole on November 11, 2022 in Wilbur-By-The-Sea, Florida.
Paul Hennessy | Anadolu Agency | Getty Images
If there is any place where the economic impact of vulnerability to climate risks is clear, it is in the Sunshine State. Even as people and businesses flood into Florida, insurance companies are heading for the hills rather than shouldering the risks of natural disasters and climate change. In June, Farmers Insurance said it would stop issuing new policies in Florida in order to “effectively manage risk exposure.” Others, including AAA, are also pulling back by not renewing some policies. The result is that the average cost of homeowners insurance jumped 33% last year, compared to 9% nationally.
2023 Infrastructure score: 227 out of 390 points (Top States grade: B)
Climate Extremes Index: 21.16%
Properties at risk: 61%
Renewable energy: 12.5%
1. Louisiana
A damaged electric line is pictured after Hurricane Ida made landfall in Louisiana, in Kenner, Louisiana, August 30, 2021.
Marco Bello | Reuters
Hurricanes are an unfortunate fact of life in the Pelican State. Louisiana was spared from major storms in 2022, and residents are knocking on wood so far in 2023. But Hurricane Ida slammed the state two years ago, making landfall near Port Fourchon as a strong Category 4 storm on the 16th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina. Ida killed 33 people in Louisiana, making it one of the deadliest storms in state history. Louisiana is at the heart of the U.S. Gulf Coast oil industry, so renewables are hardly top of mind — in fact they are not even close in America’s least sustainable state.
2023 Infrastructure score: 141 out of 390 points (Top States grade: F)
Climate Extremes Index: 23.64%
Properties at risk: 60.3%
Renewable energy: 4.1%




